Common Pediatric Dental Conditions
Black Tooth
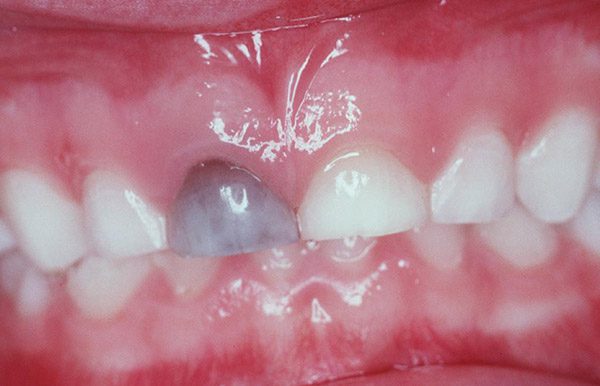 Have you noticed that one of your child’s front teeth is turning black, gray, or even purplish? They may have bumped their primary tooth. If the tooth became displaced or loosened at the time of injury, it might have reduced the blood flow, resulting in the change in color. Sometimes the tooth can lighten again, but it depends on the ongoing blood supply to the tooth.
Have you noticed that one of your child’s front teeth is turning black, gray, or even purplish? They may have bumped their primary tooth. If the tooth became displaced or loosened at the time of injury, it might have reduced the blood flow, resulting in the change in color. Sometimes the tooth can lighten again, but it depends on the ongoing blood supply to the tooth.
This condition is very common in toddlers, and no treatment is needed, aside from keeping an eye on it. Very rarely, an abscess will develop. If this happens, call us so we can see your child in the office.
If this happens to a permanent tooth, it is much more severe. Discoloration in a permanent tooth usually means the tooth is dead and a root canal is necessary.
Dental Cavity
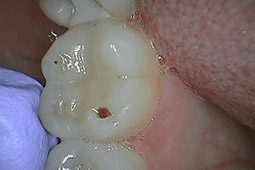 Various things can contribute to tooth decay. Improper brushing and flossing is the one parents are most familiar with, but did you know that particular germs cause decay? The germs can spread through families and last a lifetime! Tooth decay is more common in young children than asthma or diabetes.
Various things can contribute to tooth decay. Improper brushing and flossing is the one parents are most familiar with, but did you know that particular germs cause decay? The germs can spread through families and last a lifetime! Tooth decay is more common in young children than asthma or diabetes.
The germs associated with tooth decay, streptococcus mutans, feed on sugar (which is prevalent in our kids’ diets) and produce an acid that is detrimental to teeth. The bacteria and acid damage the enamel surface and deplete calcium to the area. When the affected area becomes large enough, it causes the tooth surface to collapse. This collapsed portion is a cavity.
Your best bet to limit or reduce cavities in your children is to encourage diligent brushing and flossing. Include fluoridated water during the day rather than bottled water that contains no fluoride at all. And bring your child in to see us by their first birthday!
Ask us about a FREE dental exam for children 16 months old and younger!
Double Teeth
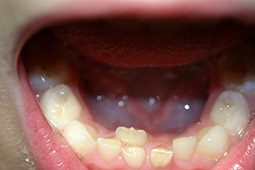 When a child’s adult tooth appears before the baby tooth falls out, this is commonly known as double, or shark, teeth. This is very common and typically does not require treatment. If the new tooth comes in and the baby tooth does not loosen, please give us a call at 623-572-9300 to make an appointment.
When a child’s adult tooth appears before the baby tooth falls out, this is commonly known as double, or shark, teeth. This is very common and typically does not require treatment. If the new tooth comes in and the baby tooth does not loosen, please give us a call at 623-572-9300 to make an appointment.
Geographic Tongue
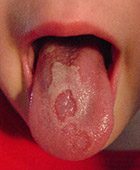 Normally, your child’s tongue is covered by tiny, pinkish-white bumps, which are actually short, fine hair-like projections (papillae). With geographic tongue, areas of the tongue are missing the papillae and appear as smooth, red patches with or without raised borders. The patches, or lesions, appear map-like, hence the name. The patches may heal in one area and develop in another place on the tongue.
Normally, your child’s tongue is covered by tiny, pinkish-white bumps, which are actually short, fine hair-like projections (papillae). With geographic tongue, areas of the tongue are missing the papillae and appear as smooth, red patches with or without raised borders. The patches, or lesions, appear map-like, hence the name. The patches may heal in one area and develop in another place on the tongue.
These lesions may look alarming, but it does not cause health problems and is not associated with oral cancer or infection. There may be slight discomfort or sensitivity to certain foods or drinks (especially tomatoes, pineapple, citrus fruits, spicy foods, walnuts, eggplant, chard, spinach, strong cheeses, oregano, or strongly flavored candies), so avoid them.
If the patches do not resolve in 7-10 days, call our office for an appointment.
Abscessed Tooth
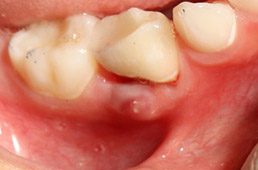 An abscessed tooth often causes a toothache with throbbing pain, bad taste in the mouth, or bad odor in the mouth. This is likely due to an infection within a tooth that has spread. The infection may cause swelling and/or a pimple on the gum that is filled with pus. The abscessed tooth may turn dark in color.
An abscessed tooth often causes a toothache with throbbing pain, bad taste in the mouth, or bad odor in the mouth. This is likely due to an infection within a tooth that has spread. The infection may cause swelling and/or a pimple on the gum that is filled with pus. The abscessed tooth may turn dark in color.
For primary teeth, treatment depends on the extent of the infection. If the infection is in the early stages and is not moving in the tooth socket, the abscess may be able to be cleared out of the pulp chamber. If the infection is advanced and the tooth is moving, the infected tooth will likely need to be removed. Untreated, the infection can spread to the bone of the jaw and other spaces. It is essential to call us if you think your child has an abscessed tooth.
Tooth Chip/Fracture
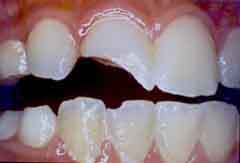
If your child chips or cracks a tooth, remain calm and call our office. The first 30 minutes after a dental accident are the most critical.
- Put a cold compress on the face to reduce swelling
- Gather the pieces of the tooth (if possible) and place them in a cup of milk
- Call the office for an appointment so we can check to make sure the chip or fracture does not extend into the root of the tooth
- Bring the pieces of the tooth with you to the office
We may be able to treat the tooth with the same material we use for tooth-colored fillings. A large fracture may require a crown, depending on your child’s age.
Tooth Intrusion
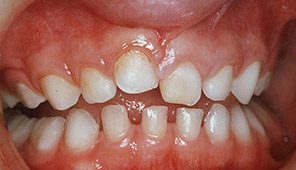 In cases when a primary tooth is pushed back up into the gum, it is called tooth intrusion. Bring your child into the office for an x-ray to check the location of the primary tooth in relation to the emerging permanent teeth. Intruded teeth usually re-emerge on their own within 2-3 months.
In cases when a primary tooth is pushed back up into the gum, it is called tooth intrusion. Bring your child into the office for an x-ray to check the location of the primary tooth in relation to the emerging permanent teeth. Intruded teeth usually re-emerge on their own within 2-3 months.
Baby teeth that have pushed up too far should be extracted to prevent damage to the adult tooth bud.
Tooth Luxation
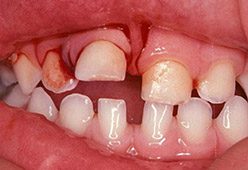 Tooth luxation is the most common type of tooth displacement for toddlers and children. During a fall, a child’s baby tooth may be pushed inward toward the palate instead of upward into the gum. This can cause a lot of bleeding, but it ultimately has less chance of damaging the developing permanent tooth.
Tooth luxation is the most common type of tooth displacement for toddlers and children. During a fall, a child’s baby tooth may be pushed inward toward the palate instead of upward into the gum. This can cause a lot of bleeding, but it ultimately has less chance of damaging the developing permanent tooth.
If a permanent tooth is displaced, try to reposition the tooth (if possible) carefully. Try to hold the tooth gently in place and call us. The first 30 minutes after the dental injury are the most critical. The teeth may reposition themselves, or the child may require orthodontic treatment. A full evaluation will reveal whether there is a fracture or if the tooth needs a splint.
Tongue/Lip Tie
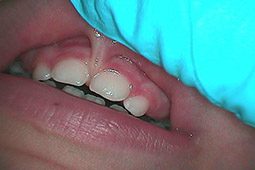 The frenum is a ‘fold’ or fibrous tissue that can restrict the motion of the lip or tongue. When it occurs with the upper lip it is referred to as a “maxillary frenum”. It can be very restrictive causing issues with breastfeeding. If a good seal cannot be maintained by the infant, air can pass into the stomach creating air pockets and potential gastric reflux. In older children, the frenum may cause a space between the incisors (diastema) and require orthodontic treatment.
The frenum is a ‘fold’ or fibrous tissue that can restrict the motion of the lip or tongue. When it occurs with the upper lip it is referred to as a “maxillary frenum”. It can be very restrictive causing issues with breastfeeding. If a good seal cannot be maintained by the infant, air can pass into the stomach creating air pockets and potential gastric reflux. In older children, the frenum may cause a space between the incisors (diastema) and require orthodontic treatment.
In the lower jaw, the frenum can severely restrict the movement of the tongue inhibiting it’s peristaltic action making breastfeeding difficult and/or painful. It may cause a poor latch, inadequate milk transfer and milk intake. This has been termed “tongue-tied” or “ankyloglossia”.
Treatment for either of these tethered conditions is called a “frenectomy/frenotomy” and is achieved with the Biolase laser. This treatment is performed chairside and sutures are not necessary.
Orthodontic Evaluation
 Dr. Tran carefully monitors dental development. She works closely with area orthodontists and will refer patients for orthodontic care at the appropriate time.
Dr. Tran carefully monitors dental development. She works closely with area orthodontists and will refer patients for orthodontic care at the appropriate time.Call 623-572-9300 or contact us with your questions or to schedule an appointment!
Toothy Riddle:
Why did the king go to the dentist?
?
(Answer Hidden Below)
Did You Know?
Snails have over 14,000 teeth, and
they are stronger than titanium!
Contact Us
Pleasant Pediatric Dentistry
9840 W Yearling Rd #1240
Peoria, AZ 85383
HOURS
Monday
8:00 AM - 5:00 PM
Tuesday
8:00 AM - 5:00 PM
Wednesday
9:00 AM - 6:00 PM
Thursday
8:00 AM - 5:00 PM
Friday
8:00 AM - 2:00 PM
